Watts to Amps Made Simple: Easy Guide for Beginners
Watts to amps is a simple but important concept if you want to understand electricity in your home or for your projects. When you know how to convert watts to amps, you can figure out how much current a device will draw from the power source. For example, a light bulb, a fan, or a microwave all use electricity differently, and knowing the amps helps you prevent overloading wires or circuits. This guide will explain the basics of watts to amps in a very easy way. You don’t need to be an engineer or a math expert to understand it. By the end, you will know how to calculate amps for DC, single-phase, and even three-phase AC circuits. Plus, we will share simple tips to make sure you can safely use electricity in your daily life.
How to Convert Watts to Amps: A Beginner-Friendly Guide
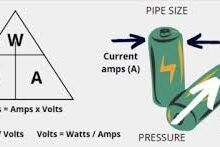
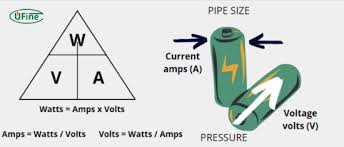
Converting watts to amps is easier than it sounds. First, you need to know the power of your device in watts and the voltage of the circuit. The simple formula is amps equals watts divided by volts. This means if you have a 1200-watt microwave and your socket is 120 volts, you divide 1200 by 120 and get 10 amps. It is important to know this because it helps you avoid overloading wires or circuits. You can use this method for DC and AC devices, but for AC devices, sometimes you also need to consider the power factor. With a little practice, converting watts to amps will feel natural, and you can quickly figure out the current for any device you use at home or in a small project.
Watts to Amps Formula Explained with Easy Examples
The formula for watts to amps is simple: Amps = Watts ÷ Volts. For example, a 60-watt light bulb on a 120-volt circuit uses 0.5 amps of current. If you have a 1000-watt heater on 240 volts, it uses 4.17 amps. By using this formula, you can calculate the current for almost any device. Knowing this helps you choose the right wires, fuses, or circuit breakers so your electrical system stays safe. It also helps when combining devices or planning battery-powered or solar projects. With real examples, learning the formula becomes easy and practical.
Single-Phase Watts to Amps: Simple Calculation Steps
Single-phase AC circuits are common in homes. To calculate watts to amps in a single-phase system, divide the device’s power in watts by the voltage multiplied by the power factor. The power factor is usually 1 for simple devices like lights. For example, a 1500-watt heater on 120 volts with a power factor of 1 draws 12.5 amps. Understanding single-phase watts to amps is useful because most household appliances run on single-phase power. It helps you pick the right circuit and ensures your devices work safely without tripping breakers or overheating wires.
Three-Phase Watts to Amps Made Easy
Three-phase circuits are used in factories or big machines. To find watts to amps in a three-phase system, the formula is a little different. You divide the power by the voltage, the square root of 3, and the power factor. For example, a 3000-watt motor on 400 volts with a power factor of 0.9 draws about 4.8 amps per phase. Knowing three-phase watts to amps is important for safe installations and maintenance. It prevents damage to equipment and ensures electricity is used efficiently.
How Power Factor Affects Your Watts to Amps Calculation
Power factor is a number between 0 and 1 that shows how efficiently a device uses electricity. If a device has a low power factor, it draws more amps than its wattage might suggest. For example, a 1000-watt device with a power factor of 0.8 draws 1.25 times more current than if the power factor were 1. Always check the power factor when calculating watts to amps for AC devices, especially big machines, to make sure wires and circuit breakers are correctly rated. Ignoring power factor can cause overheating and wasted energy.
Conclusion
Understanding watts to amps helps you use electricity safely. You can easily calculate how much current your devices need using a simple formula. This prevents overloading wires or tripping breakers.
It also makes planning projects like solar panels or battery systems simple. Knowing watts to amps keeps your home and devices safe and helps save energy.
FAQs
Q: What is the formula to convert watts to amps?
A: Amps = Watts ÷ Volts.
Q: Can I use the same formula for AC and DC?
A: Yes, but for AC, consider the power factor for accurate results.
Q: What is a power factor?
A: Power factor shows how efficiently a device uses electricity, between 0 and 1.
Q: Why is knowing amps important?
A: It helps prevent overloaded circuits, overheating wires, and tripped breakers.
Q: Can I calculate amps for three-phase devices?
A: Yes, use the three-phase formula: Amps = Watts ÷ (Voltage × √3 × Power Factor).